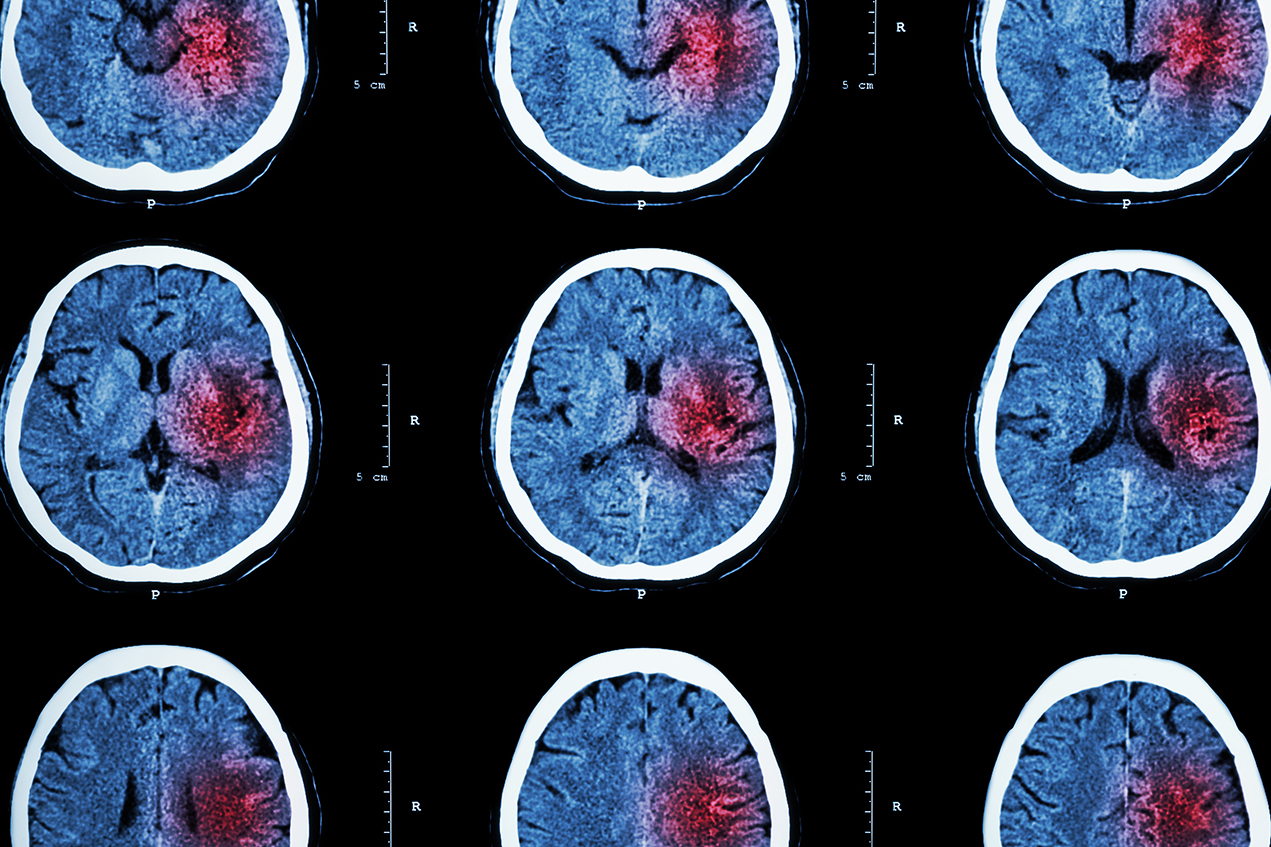
Scientists at the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute have released a newly expanded dataset of stroke patient brain scans, named the Anatomical Tracings of Lesion After Stroke (ATLAS), with the goal to advance stroke recovery research in a crucial way.
A key component of stroke research involves segmenting the image of a stroke patient’s brain lesion for proper study. Currently, this work is done manually in a process that is both time-consuming and highly specialized. With the help of expanded datasets such as ATLAS, researchers hope to more quickly develop automated lesion segmentation, which would provide stroke recovery researchers with fast, reliable segmentations to work from.
To continue reading this story, click here.